UTILITY MODEL PATENT SYSTEM FOR INDIA
he Utility model is those aspects of intellectual property rights that grant exclusive rights to the holder over his/ her inventions. It grants the holder right to prevent anyone from using his/ her invention for commercial purposes without acquiring permission to do so for a limited period of time by the right person who holds the right over the invention. The concept of Utility model protection first emerged at the Paris convention in 1883.

UTILITY MODEL PATENT SYSTEM FOR INDIA
INTRODUCTION
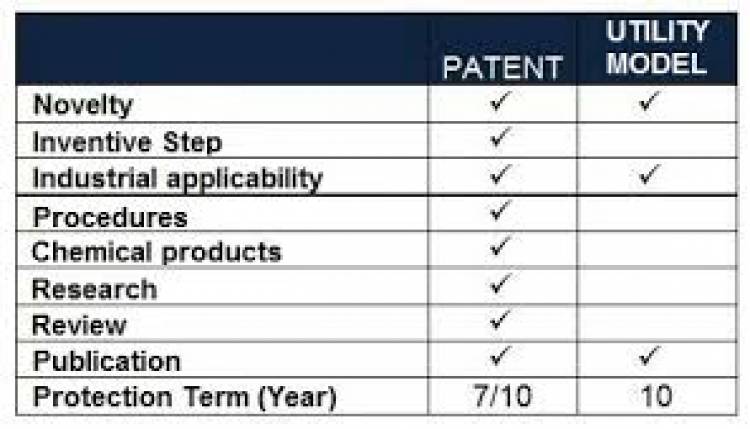
The Utility Model is those aspects of intellectual property rights that grant exclusive rights to the holder over his/ her inventions. It grants the holder right to prevent anyone from using his/ her invention for commercial purposes without acquiring permission to do so for a limited period of time by the right person who holds the right over the invention. The concept of Utility model protection first emerged at the Paris Convention in 1883. The utility model is known by many names in different countries and their laws, it is referred to as “Petty Patents”, “Short-Term Patents” and “Innovation Patents” in various intellectual property protection laws of different countries. Generally Utility model and patents seem very overlapping but there are a lot of differences between the two. The utility model is provided for the inventions which do not have the level of “inventiveness” and shows “incremental nature” for being protected as a patent and require fast registration or if there are some minor improvements or adaptions in some existing product. If any invention wants to be protected under the category of the Utility model then it must satisfy the Novelty requirement. The Term of Protection of a utility model varies from 6-15 years depending upon the jurisdiction and law made to govern such area where the utility model is acquired and is valid. In some jurisdictions, the utility model protection is only available for certain technology so invented and only the final product and not the process of making it. Due to its laws, the utility model is cheaper to obtain and easier to maintain as compared to patents.
Although there is no specific definition for the utility model or what all things can be protected under this category so, all the factors of the utility model are dependent upon the laws made by the competent authorities which are governing bodies of the intellectual property rights protection in the specific jurisdiction. But the basic concept which is “Utility model is similar to patent protection but with less duration and no examination” is the same in all the laws made in various countries. Basic guidelines set up by WIPO for any invention to be protected under the utility model are:
-
The invention must be within eligible subject matter;
-
It must be novel;
-
It must involve something innovative;
-
It must have some industrial applicability;
-
It must be described in the application incomplete way.
Utility model protection is considered very useful for the protection of inventions that make small improvements or changes to some existing product and have a short commercial life. Utility model protection system is a supplementary form of patents and industrial design protection offered by various countries like Germany, Japan, Australia, Brazil, etc. at present there are 47 countries have drafted a utility model protection system.
UTILITY MODEL PATENT SYSMENT IN INDIA
The utility model is now considered a very important aspect of intellectual property rights law for developing countries as it increases the role of local small-scale innovators and individuals in the process of economic development and also creates a competitive environment in the market. In recent years, India has emerged with various new IP laws for the protection of intellectual property rights. With several initiatives taken by the government, India now holds one of the strictest IP laws in the world according to the Indian patent act, 1970. India is emerging as a hub for small and medium scale business enterprises which basically run their business by the development of new technology or method by introducing minor improvements or changes in some existing products to meet changing market demand. The scale and medium scale enterprises provide more than 28 million people with employment. In recent years the Industrialization process in India has skyrocketed and expects even more foreign direct investments in the future because it prospers and every growing market providing opportunities to a large number of people in different ways. Thus, India needs very good IP law to ensure non-disclosure of the technology and methods so brought in by firms and further increasing new investments. The Government of India has set up a WTO cell for the small, medium and macro enterprises to increase their awareness about the IP protection system and take advantages out of it by protecting their intellectual creations as the sector is less capital intensive and creates more employment hence solving the problem on unemployment and reducing poverty and therefore is given an important place in the socio-economic development process in India. Despite all such efforts India still needs to develop laws for the protection of the Utility model which has novelty and lesser innovative steps requirement and has many benefits to satisfy the consumer and the producer in the market. Other than the patent system and design protection system currently there is no alternative system such as the utility model protection system or any such law for the protection of the IP regime in India. The small and medium sector enterprises in India lack in research and development activities due to lack of resources and investment and therefore they are engaged in the production of goods as per the basic requirement of consumers. The small and medium sector enterprises in India face a large amount of competition not only among themselves but also because of the standards of the imported goods, and therefore they are taking all the necessary steps to beat the competition and survive in the market by making variations and making improvisation for the betterment in the existing products to improve their quality to prove their existence in the market to ensure survival. But all such innovative work by the small and medium sector enterprises is undermined such small innovations are short-lived due to a large amount of competition by foreign and local competitors faced by them because of which they are unable to fulfill the requirement for patentability and industrial design as patenting needs higher degree of non-obviousness and worldwide novelty criteria. Statistical data indicates that intellectual property protection activities are very low as compared to other nations like china, south Korea, etc. in spite of higher high economic growth, expansion of the industrial sector, and good scientific manpower. All such factors prove that the current intellectual property rights laws in India are insufficient to protect or promote protection. In order to bring development to the economy, India needs to channelize local innovation to stimulate its economic growth by accommodating industrial activities at multiple levels. The protection of small and medium enterprises (MSME’s) will be promoted by granting protection to sub patentable inventions and this will also provide a solution to foreign IP. This will also help in maintaining the indigenous economy of the country which is vulnerable to copying and misappropriation both domestically and internationally. By lowering the cost of registration, patentability standards, and rights of commercial exploitation government can promote the rural industry inventions which do not meet the criteria of patents so, through this step they can be protected under the category of the utility model. The utility model system is one of the emerging aspects of protection under the patent law and its protection will be very beneficial in developing countries like India. For MSMEs which place a major role in economic growth in India, utility model protection can prove to be of great significance, since they fail to protect their inventions, and hence, they are way behind other countries in terms of business growth. Hence, the introduction of utility model rights in India will be of great significance.
BY-
GAURAV GUPTA












